The Real Reasons You Can’t Stop Food Cravings (It’s Not Willpower)
If you’ve ever said “I know what to do — I just can’t stop the cravings,”
you’re not weak.
You’re just human.
Cravings are biological, not moral.
And they can be changed once you understand the science.
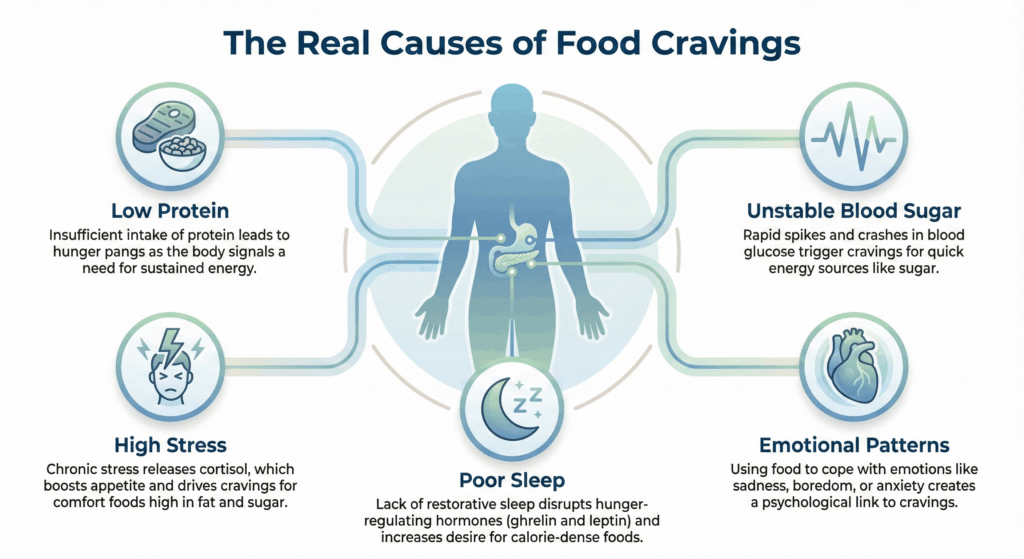
Why Do Cravings Happen?
Cravings come from a mix of:
Low protein intake
Unstable blood sugar
Poor sleep
Stress and cortisol spikes
Ultra-processed foods hijacking dopamine
Emotional patterns around comfort
When these systems are out of balance, your body creates urgent hunger signals, even if you’ve eaten enough calories.
1. Low Protein = High Cravings
Protein stabilizes hunger hormones (ghrelin, GLP-1, PYY).
When you don’t eat enough, your brain sends “Find food NOW” signals.
Protein is not optional.
It’s your biological anchor.
2. Glucose Spikes Trigger Food Noise
After a high-carb meal—especially refined carbs—blood sugar spikes and crashes.
The crash causes:
Fatigue
Anxiety
Urgent hunger
Sweet cravings
This is not a lack of discipline.
It’s chemistry.
3. Poor Sleep → Stronger Cravings
One night of bad sleep increases ghrelin by ~30%.
You wake up:
Hungrier
More impulsive
Less satisfied with food
This is why “diet starts tomorrow” often fails.
4. Stress Overrides Logic
When cortisol is high, the brain chooses:
Quick energy
Comfort foods
Familiar dopamine hits
Your biology is louder than your motivation.
Cravings Can Be Rewired
Cravings do not disappear through willpower.
They disappear through metabolic stability.
You can change cravings by changing:
Meal timing
Protein distribution
Sleep habits
How you pair carbs
Stress patterns
The quality of foods you bring home
Once biology is stable, the noise quiets.
Ready to learn how to manage cravings?
Explore the course:
Freedom From Cravings and Dieting → Click Here
FAQ: The Real Reasons You Can’t Stop Food Cravings
1. Why do I crave certain foods even after eating?
Cravings can be triggered by blood sugar dips, low protein intake, stress hormones, or emotional associations. They’re biological, not a sign of poor discipline.
2. Does protein really help reduce cravings?
Yes. Protein stabilizes hunger hormones, keeps you fuller longer, and prevents the glucose swings that trigger cravings.
3. Can sleep affect my cravings and appetite?
Absolutely. Poor sleep increases ghrelin (hunger hormone) and reduces leptin (fullness hormone), making cravings stronger and harder to control.
4. How do I stop emotional eating?
Start by stabilizing blood sugar and protein intake. Then identify emotional triggers and create replacement rituals—like movement, breathing, or journaling—before reaching for food.
5. Are cravings a sign of nutritional deficiency?
Often they are a sign of instability rather than deficiency: unstable glucose, inconsistent protein, stress, or poor sleep. Cravings make it harder to focus on true fat loss vs weight loss